The closed angle glaucoma is less common than the open angle glaucoma. Typically it causes sudden pain that, if not treated , can lead to blindness during the next 24 hours.
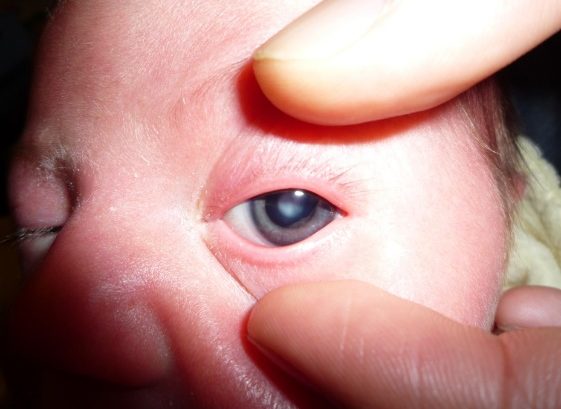
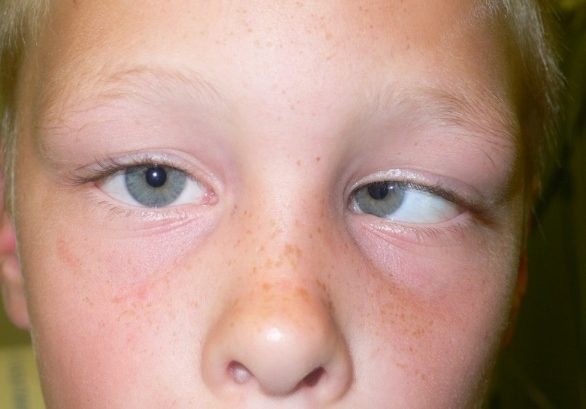
In cases of closed angle glaucoma, the iris blocks the eye’s draining system. As soon as the system is blocked the fluid that nourishes the eye cannot escape and the pressure inside the eye rises. This causes acute pain that is usually present in one eye. Other symptoms like redness, headache, nausea, pain or blurry vision can be present. In case you feel any of the above, contact with your eye doctor immediately.
In this type of glaucoma the eye’s draining system is narrow but not blocked, fact that causes a gradual increase of the eye pressure, and makes the eye prone to closed angle glaucoma. Usually both eyes have narrow draining systems. Due to the lack of symptoms you have to get your eyes regularly checked for any changes, that may be caused by narrow angle glaucoma.
- Treating closed angle glaucoma
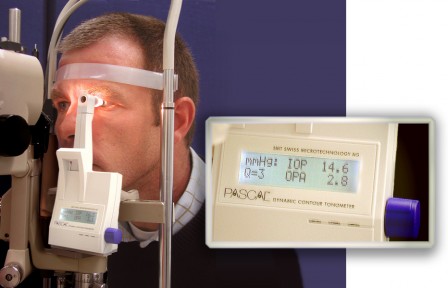
To treat the closed angle glaucoma the intraocular pressure has to immediately drop, so the optic nerve damage and the vision loss can be avoided. This includes eye drops combined with laser therapy.
Prescribing medication is ideal in cases where the intraocular pressure has to be lowered. Eye drops help at lowering the fluid production and improve the eye’s fluid draining system. Tablets or intravenous medication also help the body to reject the extra fluid.
This laser assisted method is used to bypass the eye’s blocked draining system. A small hole is opened in the periphery of the iris so the fluid can travel from the posterior to the anterior chamber of the eye. This type of therapy is also used as a preventive method for glaucoma in patients prone to glaucoma.
The whole process lasts for a few minutes
-Anesthetic eye drops are going to be placed at the affected eye
-The patient sits in front of the laser apparatus and the doctor properly focuses the laser beam on the iris
-During the procedure there is a chance of slight inconvenience or eye pain
-Patients vision may be blurry for the next few days
-The doctor will indicate when is the right time to go back to everyday activities
-The day after your treatment the doctor will measure your intraocular pressure and give you post operative instructions.